BCR (gen)
Protein regije klasterske prelomne tačke'" (BCR), znan I kao antigen bubrežnog karcinoma NY-REN-26 jest protein koji je kod ljudi kodiran genom BCR sa hromosoma 22. BCR je jedan od dva gena u kompleksu BCR-ABL, koji je povezan sa filadelfija hromosomom. Za ovaj gen su pronađene dvije varijante transkripta koje kodiraju različite izoforme.
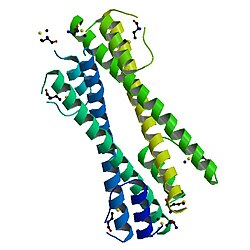
| Oligomerizacijski domen onkoproteina Bcr-Abl | |
|---|---|
 Oligomerizacijski domen strukture onkoproteina bcr-abl | |
| Identifikatori | |
| Simbol | Bcr-Abl_Oligo |
Aminokiselinska sekvenca
urediDužina polipeptidnog lanca je 1.271 aminokiselina, a molekulska težina 142.819 Da.
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MVDPVGFAEA | WKAQFPDSEP | PRMELRSVGD | IEQELERCKA | SIRRLEQEVN | ||||
| QERFRMIYLQ | TLLAKEKKSY | DRQRWGFRRA | AQAPDGASEP | RASASRPQPA | ||||
| PADGADPPPA | EEPEARPDGE | GSPGKARPGT | ARRPGAAASG | ERDDRGPPAS | ||||
| VAALRSNFER | IRKGHGQPGA | DAEKPFYVNV | EFHHERGLVK | VNDKEVSDRI | ||||
| SSLGSQAMQM | ERKKSQHGAG | SSVGDASRPP | YRGRSSESSC | GVDGDYEDAE | ||||
| LNPRFLKDNL | IDANGGSRPP | WPPLEYQPYQ | SIYVGGMMEG | EGKGPLLRSQ | ||||
| STSEQEKRLT | WPRRSYSPRS | FEDCGGGYTP | DCSSNENLTS | SEEDFSSGQS | ||||
| SRVSPSPTTY | RMFRDKSRSP | SQNSQQSFDS | SSPPTPQCHK | RHRHCPVVVS | ||||
| EATIVGVRKT | GQIWPNDGEG | AFHGDADGSF | GTPPGYGCAA | DRAEEQRRHQ | ||||
| DGLPYIDDSP | SSSPHLSSKG | RGSRDALVSG | ALESTKASEL | DLEKGLEMRK | ||||
| WVLSGILASE | ETYLSHLEAL | LLPMKPLKAA | ATTSQPVLTS | QQIETIFFKV | ||||
| PELYEIHKEF | YDGLFPRVQQ | WSHQQRVGDL | FQKLASQLGV | YRAFVDNYGV | ||||
| AMEMAEKCCQ | ANAQFAEISE | NLRARSNKDA | KDPTTKNSLE | TLLYKPVDRV | ||||
| TRSTLVLHDL | LKHTPASHPD | HPLLQDALRI | SQNFLSSINE | EITPRRQSMT | ||||
| VKKGEHRQLL | KDSFMVELVE | GARKLRHVFL | FTDLLLCTKL | KKQSGGKTQQ | ||||
| YDCKWYIPLT | DLSFQMVDEL | EAVPNIPLVP | DEELDALKIK | ISQIKNDIQR | ||||
| EKRANKGSKA | TERLKKKLSE | QESLLLLMSP | SMAFRVHSRN | GKSYTFLISS | ||||
| DYERAEWREN | IREQQKKCFR | SFSLTSVELQ | MLTNSCVKLQ | TVHSIPLTIN | ||||
| KEDDESPGLY | GFLNVIVHSA | TGFKQSSNLY | CTLEVDSFGY | FVNKAKTRVY | ||||
| RDTAEPNWNE | EFEIELEGSQ | TLRILCYEKC | YNKTKIPKED | GESTDRLMGK | ||||
| GQVQLDPQAL | QDRDWQRTVI | AMNGIEVKLS | VKFNSREFSL | KRMPSRKQTG | ||||
| VFGVKIAVVT | KRERSKVPYI | VRQCVEEIER | RGMEEVGIYR | VSGVATDIQA | ||||
| LKAAFDVNNK | DVSVMMSEMD | VNAIAGTLKL | YFRELPEPLF | TDEFYPNFAE | ||||
| GIALSDPVAK | ESCMLNLLLS | LPEANLLTFL | FLLDHLKRVA | EKEAVNKMSL | ||||
| HNLATVFGPT | LLRPSEKESK | LPANPSQPIT | MTDSWSLEVM | SQVQVLLYFL | ||||
| QLEAIPAPDS | KRQSILFSTE | V |
Struktura
urediDomen oligomerizacije onkoproteina BCR-ABL koji se nalazi na N-terminalu BCR je od suštinskog značaja za onkogenost fuzijskog protein BCR-ABL. Domen oligomerizacije onkoproteina BCR-ABL sastoji se od kratkog N-terminalnog alfa-heliksa (alfa-1), fleksibilne petlje i dugog C-terminalnog heliksa (alfa-2). Oni zajedno formiraju strukturu u obliku slova N, sa petljom koja omogućava da dva heliksa zauzmu paralelnu orijentaciju. Monomerni domeni povezuju se u dimer, m antiparalelne upredene zavojnice između alfa-heliksa -2 i domena zamjena dva alfa-1 heliksa, pri čemu se jedan alfa-1 heliks okreće unazad i nabije na alfa-2 heliks iz drugog monomera. Dva dimera se zatim povezuju u tetramer.[5]
Funkcija
urediIako je BCR-ABL fuzijski protein proučavan bezbroj puta, funkcija normalnog BCR genskog proizvoda još uvijek nije jasna. Protein ima aktivnost serin/treonin kinaza i faktora izmjene gvanin-nukleotida za porodicu Rho GTPaza, uključujući RhoA.[6][7]
Klinički značaj
urediRecipročna translokacija između hromosoma 22 i 9 proizvodi filadelfija hromosom], koji se često nalazi kod pacijenata sa hroničnom mijelogenom leukemijom. Prelomna tačka hromosoma 22 za ovu translokaciju nalazi se unutar gena "BCR". Translokacija proizvodi fuzijski protein koji je kodiran sekvencom iz "BCR" i "ABL", gena na tački prekida hromosoma 9.[8]
Interakcije
urediPokazalo se da BCR protein u interakciji sa:
Također pogledajte
urediReference
uredi- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000186716 - Ensembl, maj 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000009681 - Ensembl, maj 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Zhao X, Ghaffari S, Lodish H, Malashkevich VN, Kim PS (February 2002). "Structure of the Bcr-Abl oncoprotein oligomerization domain". Nat. Struct. Biol. 9 (2): 117–20. doi:10.1038/nsb747. PMID 11780146. S2CID 17453012.
- ^ Dubash, Adi D.; Koetsier, Jennifer L.; Amargo, Evangeline V.; Najor, Nicole A.; Harmon, Robert M.; Green, Kathleen J. (2013-08-19). "The GEF Bcr activates RhoA/MAL signaling to promote keratinocyte differentiation via desmoglein-1". The Journal of Cell Biology. 202 (4): 653–666. doi:10.1083/jcb.201304133. ISSN 0021-9525. PMC 3747303. PMID 23940119.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: Breakpoint cluster region".
- ^ "Entrez Gene: BCR breakpoint cluster region".
- ^ a b c Puil L, Liu J, Gish G, Mbamalu G, Bowtell D, Pelicci PG, Arlinghaus R, Pawson T (February 1994). "Bcr-Abl oncoproteins bind directly to activators of the Ras signalling pathway". EMBO J. 13 (4): 764–73. doi:10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06319.x. PMC 394874. PMID 8112292.
- ^ Ling X, Ma G, Sun T, Liu J, Arlinghaus RB (January 2003). "Bcr and Abl interaction: oncogenic activation of c-Abl by sequestering Bcr". Cancer Res. 63 (2): 298–303. PMID 12543778.
- ^ Pendergast AM, Muller AJ, Havlik MH, Maru Y, Witte ON (July 1991). "BCR sequences essential for transformation by the BCR-ABL oncogene bind to the ABL SH2 regulatory domain in a non-phosphotyrosine-dependent manner". Cell. 66 (1): 161–71. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(91)90148-R. PMID 1712671. S2CID 9933891.
- ^ Hallek M, Danhauser-Riedl S, Herbst R, Warmuth M, Winkler A, Kolb HJ, Druker B, Griffin JD, Emmerich B, Ullrich A (July 1996). "Interaction of the receptor tyrosine kinase p145c-kit with the p210bcr/abl kinase in myeloid cells". Br. J. Haematol. 94 (1): 5–16. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2141.1996.6102053.x. PMID 8757502. S2CID 30033345.
- ^ a b c d Bai RY, Jahn T, Schrem S, Munzert G, Weidner KM, Wang JY, Duyster J (August 1998). "The SH2-containing adapter protein GRB10 interacts with BCR-ABL". Oncogene. 17 (8): 941–8. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202024. PMID 9747873. S2CID 20866214.
- ^ a b Million RP, Harakawa N, Roumiantsev S, Varticovski L, Van Etten RA (June 2004). "A direct binding site for Grb2 contributes to transformation and leukemogenesis by the Tel-Abl (ETV6-Abl) tyrosine kinase". Mol. Cell. Biol. 24 (11): 4685–95. doi:10.1128/MCB.24.11.4685-4695.2004. PMC 416425. PMID 15143164.
- ^ Heaney C, Kolibaba K, Bhat A, Oda T, Ohno S, Fanning S, Druker BJ (January 1997). "Direct binding of CRKL to BCR-ABL is not required for BCR-ABL transformation". Blood. 89 (1): 297–306. doi:10.1182/blood.V89.1.297. PMID 8978305.
- ^ Kolibaba KS, Bhat A, Heaney C, Oda T, Druker BJ (March 1999). "CRKL binding to BCR-ABL and BCR-ABL transformation". Leuk. Lymphoma. 33 (1–2): 119–26. doi:10.3109/10428199909093732. PMID 10194128.
- ^ Lionberger JM, Smithgall TE (February 2000). "The c-Fes protein-tyrosine kinase suppresses cytokine-independent outgrowth of myeloid leukemia cells induced by Bcr-Abl". Cancer Res. 60 (4): 1097–103. PMID 10706130.
- ^ a b c Maru Y, Peters KL, Afar DE, Shibuya M, Witte ON, Smithgall TE (February 1995). "Tyrosine phosphorylation of BCR by FPS/FES protein-tyrosine kinases induces association of BCR with GRB-2/SOS". Mol. Cell. Biol. 15 (2): 835–42. doi:10.1128/MCB.15.2.835. PMC 231961. PMID 7529874.
- ^ Million RP, Van Etten RA (July 2000). "The Grb2 binding site is required for the induction of chronic myeloid leukemia-like disease in mice by the Bcr/Abl tyrosine kinase". Blood. 96 (2): 664–70. doi:10.1182/blood.V96.2.664. PMID 10887132.
- ^ Ma G, Lu D, Wu Y, Liu J, Arlinghaus RB (May 1997). "Bcr phosphorylated on tyrosine 177 binds Grb2". Oncogene. 14 (19): 2367–72. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1201053. PMID 9178913. S2CID 9249479.
- ^ Stanglmaier M, Warmuth M, Kleinlein I, Reis S, Hallek M (February 2003). "The interaction of the Bcr-Abl tyrosine kinase with the Src kinase Hck is mediated by multiple binding domains". Leukemia. 17 (2): 283–9. doi:10.1038/sj.leu.2402778. PMID 12592324. S2CID 8695384.
- ^ Lionberger JM, Wilson MB, Smithgall TE (June 2000). "Transformation of myeloid leukemia cells to cytokine independence by Bcr-Abl is suppressed by kinase-defective Hck". J. Biol. Chem. 275 (24): 18581–5. doi:10.1074/jbc.C000126200. PMID 10849448.
- ^ Radziwill G, Erdmann RA, Margelisch U, Moelling K (July 2003). "The Bcr kinase downregulates Ras signaling by phosphorylating AF-6 and binding to its PDZ domain". Mol. Cell. Biol. 23 (13): 4663–72. doi:10.1128/MCB.23.13.4663-4672.2003. PMC 164848. PMID 12808105.
- ^ a b Salgia R, Sattler M, Pisick E, Li JL, Griffin JD (February 1996). "p210BCR/ABL induces formation of complexes containing focal adhesion proteins and the protooncogene product p120c-Cbl". Exp. Hematol. 24 (2): 310–3. PMID 8641358.
- ^ Salgia R, Li JL, Lo SH, Brunkhorst B, Kansas GS, Sobhany ES, Sun Y, Pisick E, Hallek M, Ernst T (March 1995). "Molecular cloning of human paxillin, a focal adhesion protein phosphorylated by P210BCR/ABL". J. Biol. Chem. 270 (10): 5039–47. doi:10.1074/jbc.270.10.5039. PMID 7534286.
- ^ Skorski T, Kanakaraj P, Nieborowska-Skorska M, Ratajczak MZ, Wen SC, Zon G, Gewirtz AM, Perussia B, Calabretta B (July 1995). "Phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase activity is regulated by BCR/ABL and is required for the growth of Philadelphia chromosome-positive cells". Blood. 86 (2): 726–36. doi:10.1182/blood.V86.2.726.bloodjournal862726. PMID 7606002.
- ^ Liedtke M, Pandey P, Kumar S, Kharbanda S, Kufe D (October 1998). "Regulation of Bcr-Abl-induced SAP kinase activity and transformation by the SHPTP1 protein tyrosine phosphatase". Oncogene. 17 (15): 1889–92. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1202117. PMID 9788431. S2CID 42228230.
- ^ Park AR, Oh D, Lim SH, Choi J, Moon J, Yu DY, Park SG, Heisterkamp N, Kim E, Myung PK, Lee JR (2012). "Regulation of dendritic arborization by BCR Rac1 GTPase-activating protein, a substrate of PTPRT". J. Cell Sci. 125 (Pt 19): 4518–31. doi:10.1242/jcs.105502. PMID 22767509. S2CID 22422544.
- ^ Takeda N, Shibuya M, Maru Y (January 1999). "The BCR-ABL oncoprotein potentially interacts with the xeroderma pigmentosum group B protein". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 96 (1): 203–7. Bibcode:1999PNAS...96..203T. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.1.203. PMC 15117. PMID 9874796.
Dopunska literatura
urediVanjski linkovi
uredi- BCR protein, human na US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Lokacija ljudskog genoma BCR i stranica sa detaljima o genu BCR u UCSC Genome Browseru.
- P11274