IGJ
J lanac imunoglobulina jest proteinska komponenta antitijela IgM i IgA, koji je kod ljudi kodiran genom IGJ sa hromosoma 4.[5] Ima 137 polipeptidnih ostataka.[6][7][8][9]
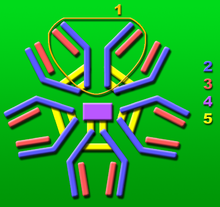
1: Bazna jedinica.
2: Teški lanci.
3: lLahki lanci.
4: J-lanac.
5: Međumolekulske disulfidne veze.

Aminokiselinska sekvenca
urediDužina polipeptidnog lanca je 159 aminokiselina, а molekulska težina 18 099 Da.[10]
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MKNHLLFWGV | LAVFIKAVHV | KAQEDERIVL | VDNKCKCARI | TSRIIRSSED | ||||
| PNEDIVERNI | RIIVPLNNRE | NISDPTSPLR | TRFVYHLSDL | CKKCDPTEVE | ||||
| LDNQIVTATQ | SNICDEDSAT | ETCYTYDRNK | CYTAVVPLVY | GGETKMVETA | ||||
| LTPDACYPD |
Struktura
urediMolekulska težina J lanca je približno 15 kDa. Pokazuje standardnu imunoglobulinsku strukturu savijanja od dva [beta-list|[β-savijena lista]] od četiri trake presavijene jedna uz drugu. Ima osam cisteinskih ostataka. Dva od ovih ostataka povezuju α lance IgA ili μ lance IgM preko disulfidnog mosta, efektivno služe kao "ljepilo" između dva Fc regiona antitijela.[11]
J-lanac pokazuje veliki stepen homologije između ptičjih vrsta i ljudi, sugerirajući da ima važnu funkciju.[11]
Funkcija
urediJ lanac je potreban da bi se IgM ili IgA izlučili u sluznicu.[6] Kao dio polimernog imunoglobulina (pIg), J-lanac je neophodan za vezivanje pIg za pIgR, koji formira sekretornu komponentu, nakon izlučivanja sekretornog pIg iz epitelnih ćelija.[12] Ovo vezivanje olakšava transport J-lanca pozitivnih pIg molekula od baznih do apikalnih strana epitelnih ćelija.
Budući da su IgM i IgA dva jedine+a tipa dvije antitijela koja polimeriziraju, početne hipoteze su navodile da je J-lanac potreban za polimerizaciju. Međutim, naknadno je otkriveno da IgM može polimerizirati u odsustvu J-lanca i kao pentamer i heksamer, međutim, oba postoje u manjem broju u organizmima kojima nedostaju J-lanci. U takvim slučajevima ima i manje IgA dimera.[6]
J-lanac također ima ulogu u aktivaciji komplementa. J-lančani negativni IgM heksameri su 15-20 puta efikasniji u aktiviranju komplementa od J-lanca pozitivnih IgM pentamera.[12] Posljedica ovog nedostatka aktivacije komplementa je da omogućava J-lancu pozitivnog pIgM da veže antigene bez izazivanja pretjeranog oštećenja epitelnih membrana u aktivaciji komplementa.
Reference
uredi- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000132465 - Ensembl, maj 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000067149 - Ensembl, maj 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Levinson (2014). Medical Microbiology and Immunology (11 izd.). McGrawHill. str. 405–6.
- ^ a b c Schroeder, Harry; Wald, David; Greenspan, Neil (2008). "Chapter 4: Immunoglobulins: Structure and Function". u Paul, William (ured.). Fundamental Immunology (Book) (6th izd.). Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. str. 125–151. ISBN 978-0-7817-6519-0.
- ^ Max EE, McBride OW, Morton CC, Robinson MA (Sep 1986). "Human J chain gene: chromosomal localization and associated restriction fragment length polymorphisms". Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 83 (15): 5592–6. Bibcode:1986PNAS...83.5592M. doi:10.1073/pnas.83.15.5592. PMC 386334. PMID 3016707.
- ^ Max EE, Korsmeyer SJ (maj 1985). "Human J chain gene. Structure and expression in B lymphoid cells". J Exp Med. 161 (4): 832–49. doi:10.1084/jem.161.4.832. PMC 2189063. PMID 2984306.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: IGJ immunoglobulin J polypeptide, linker protein for immunoglobulin alpha and mu polypeptides".
- ^ "UniProt, P01591" (jezik: engleski). Pristupljeno 28. 10. 2021.
- ^ a b Kiyono, Hiroshi; Kunisawa, Jaw; McGhee, Jerry; Mestecky, Jiri (2008). "Chapter 31: The Mucosal Immune System". u Paul, William (ured.). Fundamental Immunology (Book) (6th izd.). Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. str. 983–1030. ISBN 978-0-7817-6519-0.
- ^ a b Johansen FE, Braathen R, Brandtzaeg P (septembar 2000). "Role of J Chain in Secretory Immunoglobulin Formation". Scandinavian Journal of Immunology. 52 (3): 240–248. doi:10.1046/j.1365-3083.2000.00790.x. PMID 10972899. S2CID 5958810.
Dopunska literatura
uredi- Koshland ME (1986). "The coming of age of the immunoglobulin J chain". Annu. Rev. Immunol. 3: 425–53. doi:10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.002233. PMID 2415140.
- Tartakoff A, Vassalli P (1980). "Plasma cell immunoglobulin M molecules. Their biosynthesis, assembly, and intracellular transport". J. Cell Biol. 83 (2 Pt 1): 284–99. doi:10.1083/jcb.83.2.284. PMC 2111544. PMID 115892.
- Mole JE, Bhown AS, Bennett JC (1977). "Primary structure of human J chain: alignment of peptides from chemical and enzymatic hydrolyses". Biochemistry. 16 (16): 3507–13. doi:10.1021/bi00635a002. PMID 407930.
- Bastian A, Kratzin H, Eckart K, Hilschmann N (1993). "Intra- and interchain disulfide bridges of the human J chain in secretory immunoglobulin A.". Biol. Chem. Hoppe-Seyler. 373 (12): 1255–63. doi:10.1515/bchm3.1992.373.2.1255. PMID 1292512.
- Frutiger S, Hughes GJ, Paquet N, et al. (1993). "Disulfide bond assignment in human J chain and its covalent pairing with immunoglobulin M.". Biochemistry. 31 (50): 12643–7. doi:10.1021/bi00165a014. PMID 1472500.
- Moro I, Iwase T, Komiyama K, et al. (1990). "Immunoglobulin A (IgA) polymerization sites in human immunocytes: immunoelectron microscopic study". Cell Struct. Funct. 15 (2): 85–91. doi:10.1247/csf.15.85. PMID 2113434.
- Alberini CM, Bet P, Milstein C, Sitia R (1990). "Secretion of immunoglobulin M assembly intermediates in the presence of reducing agents". Nature. 347 (6292): 485–7. Bibcode:1990Natur.347..485A. doi:10.1038/347485a0. PMID 2120591. S2CID 4348113.
- Sumi Y, Nagura H, Kaneda T, Oka T (1989). "Immunoelectron microscopical localization of immunoglobulins, secretory component and J chain in the human minor salivary glands". Journal of Oral Pathology and Medicine. 17 (8): 390–5. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0714.1988.tb01303.x. PMID 3146624.
- Hajdu I, Moldoveanu Z, Cooper MD, Mestecky J (1984). "Ultrastructural studies of human lymphoid cells. mu and J chain expression as a function of B cell differentiation". J. Exp. Med. 158 (6): 1993–2006. doi:10.1084/jem.158.6.1993. PMC 2187181. PMID 6417260.
- Yasuda N, Kanoh T, Uchino H (1980). "J chain synthesis in human myeloma cells: light and electron microscopic studies". Clin. Exp. Immunol. 40 (3): 573–80. PMC 1538946. PMID 6774844.
- Harper SJ, Allen AC, Béné MC, et al. (1995). "Increased dimeric IgA-producing B cells in tonsils in IgA nephropathy determined by in situ hybridization for J chain mRNA". Clin. Exp. Immunol. 101 (3): 442–8. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2249.1995.tb03132.x. PMC 1553245. PMID 7664491.
- Iwase T, Saito I, Takahashi T, et al. (1994). "Early expression of human J chain and mu chain gene in the fetal liver". Cell Struct. Funct. 18 (5): 297–302. doi:10.1247/csf.18.297. PMID 8168154.
- Harper SJ, Pringle JH, Wicks AC, et al. (1994). "Expression of J chain mRNA in duodenal IgA plasma cells in IgA nephropathy". Kidney Int. 45 (3): 836–44. doi:10.1038/ki.1994.110. PMID 8196286.
- Bjercke S, Brandtzaeg P (1994). "Glandular distribution of immunoglobulins, J chain, secretory component, and HLA-DR in the human endometrium throughout the menstrual cycle". Hum. Reprod. 8 (9): 1420–5. doi:10.1093/oxfordjournals.humrep.a138271. PMID 8253928.
- Bertrand FE, Billips LG, Gartland GL, et al. (1996). "The J chain gene is transcribed during B and T lymphopoiesis in humans". J. Immunol. 156 (11): 4240–4. PMID 8666793.
- Atkin JD, Pleass RJ, Owens RJ, Woof JM (1996). "Mutagenesis of the human IgA1 heavy chain tailpiece that prevents dimer assembly". J. Immunol. 157 (1): 156–9. PMID 8683109.
- Strausberg RL, Feingold EA, Grouse LH, et al. (2003). "Generation and initial analysis of more than 15,000 full-length human and mouse cDNA sequences". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 99 (26): 16899–903. doi:10.1073/pnas.242603899. PMC 139241. PMID 12477932.