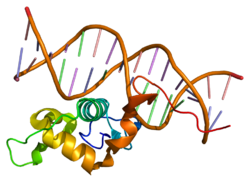
NR4A2
Jedarni receptor 4A2 (NR4A2) (član 2 grupe A potporodice 4 jedarnih receptora), znan i kao jedarni receptor srodan proteinu 1 (NURR1) jest protein koji je kod ljudi kodiran genom NR4A2 sa hromosoma 2.[5] NR4A2 je član porodice jedarnih receptora unutarćelijskih transkripcijskih faktora.
Amiokiselininska sekvenca
urediDužina polipeptidnog lanca je 598 aminokiselina, a molekulska težina 66.591 Da.[6].
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPCVQAQYGS | SPQGASPASQ | SYSYHSSGEY | SSDFLTPEFV | KFSMDLTNTE | ||||
| ITATTSLPSF | STFMDNYSTG | YDVKPPCLYQ | MPLSGQQSSI | KVEDIQMHNY | ||||
| QQHSHLPPQS | EEMMPHSGSV | YYKPSSPPTP | TTPGFQVQHS | PMWDDPGSLH | ||||
| NFHQNYVATT | HMIEQRKTPV | SRLSLFSFKQ | SPPGTPVSSC | QMRFDGPLHV | ||||
| PMNPEPAGSH | HVVDGQTFAV | PNPIRKPASM | GFPGLQIGHA | SQLLDTQVPS | ||||
| PPSRGSPSNE | GLCAVCGDNA | ACQHYGVRTC | EGCKGFFKRT | VQKNAKYVCL | ||||
| ANKNCPVDKR | RRNRCQYCRF | QKCLAVGMVK | EVVRTDSLKG | RRGRLPSKPK | ||||
| SPQEPSPPSP | PVSLISALVR | AHVDSNPAMT | SLDYSRFQAN | PDYQMSGDDT | ||||
| QHIQQFYDLL | TGSMEIIRGW | AEKIPGFADL | PKADQDLLFE | SAFLELFVLR | ||||
| LAYRSNPVEG | KLIFCNGVVL | HRLQCVRGFG | EWIDSIVEFS | SNLQNMNIDI | ||||
| SAFSCIAALA | MVTERHGLKE | PKRVEELQNK | IVNCLKDHVT | FNNGGLNRPN | ||||
| YLSKLLGKLP | ELRTLCTQGL | QRIFYLKLED | LVPPPAIIDK | LFLDTLPF |
Struktura
urediJedno istraživanje poučavalo je strukture i otkrilo da NR4A2 ne sadrži šupljinu koja se vezuje za ligand, već deo ispunjen hidrofobnim bočnim lancima. Nepolarni aminokiselinski ostaci koregulatora NR4A2, SMRT i NCoR, vezuju se za ovaj hidrofobni flaster. Analiza tercijarne strukture pokazala je da se vezna površina domena za vezivanje liganda nalazi na žljebovima 11. i 12. alfa-heliksa. Ova studija je takođe otkrila da su bitne strukturne komponente ovog hidrofobnog flastera tri aminokiselinska ostatka, F574, F592, L593; mutacija bilo koje od njih inhibira aktivnost LBD.[7]
Funkcija
urediNR4A2 ima ključnu ulogu u održavanju dopaminskog sistema mozga.[[8] Mutacije ovog gena povezane su s poremećajima povezanim s dopaminergijskom disfunkcijom, uključujući Parkinsonovu bolest i shizofreniju. Pogrešna regulacija ovog gena može biti povezana sa reumatoidnim artritisom. Za ovaj gen, identificirane su četiri varijante transkripta koje kodiraju četiri različite izoforme. Mogu postojati dodatne alternativne varijante prerade, ali njihova priroda pune dužine nije utvrđena.[9]
Smatra se da je ovaj protein kritičan za razvoj dopaminskog fenotipa u srednjem mozgu, jer miševima bez NR4A2 nedostaje ekspresija ovog fenotipa. Ovo dalje potvrđuju studije koje pokazuju da kada se forsira ekspresija NR4A2 u nevinim prekursorskim ćelijama, postoji potpuna ekspresija fenotipa dopaminskog gena.[10]
Iako je NR4A2 ključni protein, postoje i drugi faktori koji su potrebni jer istraživanja pokazuju da samo ekspresija NR4A2 ne može stimulirati fenotipsku ekspresiju ovog gena. Jedan od ovih predloženih faktora je transkripcijski faktor 2 (Foxa2). Studije su otkrile da su ova dva faktora unutar istog regiona razvoja dopamibnskih neurona, oba ova faktora su bila prisutna da bi imali ekspresiju za dopaminski fenotip.
Aplikacije
urediNR4A2 indukuje ekspresiju tirozin-hidroksilaze (TH), što na kraju dovodi do diferencijacije u dopaminergne neurone. Pokazalo se da NR4A2 indukuje diferencijaciju u ćelijma prekursora CNS-a in vitro, ali su im potrebni dodatni faktori za postizanje pune zrelosti i dopaminergijsku diferencijaciju..[11] Stoga, modulacija NR4A2 može biti obećavajuća za stvaranje dopaminergiiskih neurona za istraživanje Parkinsonove bolesti, ali implantacija ovih induciranih ćelija kao terapijskih tretmana ima ograničene rezultate.
Studije nokauta
urediStudije su pokazale da heterozigotni nokaut-miševi za gen NR4A2 pokazuju smanjeno oslobađanje dopamina. U početku je to kompenzirano smanjenjem stope ponovnog uzimanja dopamina; međutim, s vremenom ovo ponovno preuzimanje nije moglo nadoknaditi smanjenu količinu dopamina koji se oslobađa. Zajedno sa gubitkom neuronskih receptora dopamina, ovo može dovesti do pojave simptoma Parkinsonove bolesti.[12]
Interakcije
urediPokazalo se da je NR4A2 u interakciji sa:
Reference
uredi- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000153234 - Ensembl, maj 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000026826 - Ensembl, maj 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Okabe T, Takayanagi R, Imasaki K, Haji M, Nawata H, Watanabe T (april 1995). "cDNA cloning of a NGFI-B/nur77-related transcription factor from an apoptotic human T cell line". Journal of Immunology. 154 (8): 3871–9. PMID 7706727.
- ^ "UniProt, P43354" (jezik: engleski). Pristupljeno 18. 11. 2021.
- ^ Codina A, Benoit G, Gooch JT, Neuhaus D, Perlmann T, Schwabe JW (decembar 2004). "Identification of a novel co-regulator interaction surface on the ligand binding domain of Nurr1 using NMR footprinting". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 279 (51): 53338–45. doi:10.1074/jbc.M409096200. PMID 15456745.
- ^ Sacchetti P, Carpentier R, Ségard P, Olivé-Cren C, Lefebvre P (2006). "Multiple signaling pathways regulate the transcriptional activity of the orphan nuclear receptor NURR1". Nucleic Acids Research. 34 (19): 5515–27. doi:10.1093/nar/gkl712. PMC 1636490. PMID 17020917.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: NR4A2 nuclear receptor subfamily 4, group A, member 2".
- ^ Yi, Sang-Hoon; He, Xi-Biao; Rhee, Yong-Hee; Park, Chang-Hwan; Takizawa, Takumi; Nakashima, Kinichi; Lee, Sang-Hun (15. 2. 2014). "Foxa2 Acts as a Co-activator Potentiating Expression of the Nurr1-induced DA Phenotype via Epigenetic Regulation". Development. 141 (4): 761–772. doi:10.1242/dev.095802. PMID 24496614. S2CID 16677797.
- ^ Kim JY, Koh HC, Lee JY, Chang MY, Kim YC, Chung HY, Son H, Lee YS, Studer L, McKay R, Lee SH (juni 2003). "Dopaminergic neuronal differentiation from rat embryonic neural precursors by Nurr1 overexpression". Journal of Neurochemistry. 85 (6): 1443–54. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.01780.x. PMID 12787064. S2CID 21991471.
- ^ Zhang L, Le W, Xie W, Dani JA (maj 2012). "Age-related changes in dopamine signaling in Nurr1 deficient mice as a model of Parkinson's disease". Neurobiology of Aging. 33 (5): 1001.e7–16. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.03.022. PMC 3155628. PMID 21531044.
- ^ Zhang L, Cen L, Qu S, Wei L, Mo M, Feng J, Sun C, Xiao Y, Luo Q, Li S, Yang X, Xu P (Apr 2016). "Enhancing Beta-Catenin Activity via GSK3beta Inhibition Protects PC12 Cells against Rotenone Toxicity through Nurr1 Induction". PLOS ONE. 11 (4): e0152931. Bibcode:2016PLoSO..1152931Z. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0152931. PMC 4821554. PMID 27045591.
- ^ Jacobs FM, van Erp S, van der Linden AJ, von Oerthel L, Burbach JP, Smidt MP (februar 2009). "Pitx3 potentiates Nurr1 in dopamine neuron terminal differentiation through release of SMRT-mediated repression". Development. 136 (4): 531–40. doi:10.1242/dev.029769. PMID 19144721.
- ^ a b Perlmann T, Jansson L (april 1995). "A novel pathway for vitamin A signaling mediated by RXR heterodimerization with NGFI-B and NURR1". Genes & Development. 9 (7): 769–82. doi:10.1101/gad.9.7.769. PMID 7705655.
Dopunska literatura
uredi- Le W, Appel SH (februar 2004). "Mutant genes responsible for Parkinson's disease". Current Opinion in Pharmacology. 4 (1): 79–84. doi:10.1016/j.coph.2003.09.005. PMID 15018843.
- Wedler B, Wüstenberg PW, Naumann G (juli 1975). "[Treatment of hypertonus in diabetes mellitus]". Zeitschrift für die Gesamte Innere Medizin und Ihre Grenzgebiete. 30 (13): 437–42. PMID 4929.
- Perlmann T, Jansson L (april 1995). "A novel pathway for vitamin A signaling mediated by RXR heterodimerization with NGFI-B and NURR1". Genes & Development. 9 (7): 769–82. doi:10.1101/gad.9.7.769. PMID 7705655.
- Forman BM, Umesono K, Chen J, Evans RM (maj 1995). "Unique response pathways are established by allosteric interactions among nuclear hormone receptors". Cell. 81 (4): 541–50. doi:10.1016/0092-8674(95)90075-6. PMID 7758108. S2CID 3203590.
- Mages HW, Rilke O, Bravo R, Senger G, Kroczek RA (novembar 1994). "NOT, a human immediate-early response gene closely related to the steroid/thyroid hormone receptor NAK1/TR3". Molecular Endocrinology. 8 (11): 1583–91. doi:10.1210/me.8.11.1583. PMID 7877627.
- Maruyama K, Sugano S (januar 1994). "Oligo-capping: a simple method to replace the cap structure of eukaryotic mRNAs with oligoribonucleotides". Gene. 138 (1–2): 171–4. doi:10.1016/0378-1119(94)90802-8. PMID 8125298.
- Suzuki Y, Yoshitomo-Nakagawa K, Maruyama K, Suyama A, Sugano S (oktobar 1997). "Construction and characterization of a full length-enriched and a 5'-end-enriched cDNA library". Gene. 200 (1–2): 149–56. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(97)00411-3. PMID 9373149.
- Torii T, Kawarai T, Nakamura S, Kawakami H (april 1999). "Organization of the human orphan nuclear receptor Nurr1 gene". Gene. 230 (2): 225–32. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(99)00064-5. PMID 10216261.
- Ichinose H, Ohye T, Suzuki T, Sumi-Ichinose C, Nomura T, Hagino Y, Nagatsu T (april 1999). "Molecular cloning of the human Nurr1 gene: characterization of the human gene and cDNAs". Gene. 230 (2): 233–9. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(99)00065-7. PMID 10216262.
- Chen YH, Tsai MT, Shaw CK, Chen CH (decembar 2001). "Mutation analysis of the human NR4A2 gene, an essential gene for midbrain dopaminergic neurogenesis, in schizophrenic patients". American Journal of Medical Genetics. 105 (8): 753–7. doi:10.1002/ajmg.10036. PMID 11803525.
- Ishiguro H, Okubo Y, Ohtsuki T, Yamakawa-Kobayashi K, Arinami T (januar 2002). "Mutation analysis of the retinoid X receptor beta, nuclear-related receptor 1, and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha genes in schizophrenia and alcohol dependence: possible haplotype association of nuclear-related receptor 1 gene to alcohol dependence". American Journal of Medical Genetics. 114 (1): 15–23. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1620. PMID 11840500.
- McEvoy AN, Murphy EA, Ponnio T, Conneely OM, Bresnihan B, FitzGerald O, Murphy EP (mart 2002). "Activation of nuclear orphan receptor NURR1 transcription by NF-kappa B and cyclic adenosine 5'-monophosphate response element-binding protein in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue". Journal of Immunology. 168 (6): 2979–87. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.168.6.2979. PMID 11884470.
- Xu PY, Liang R, Jankovic J, Hunter C, Zeng YX, Ashizawa T, Lai D, Le WD (mart 2002). "Association of homozygous 7048G7049 variant in the intron six of Nurr1 gene with Parkinson's disease". Neurology. 58 (6): 881–4. doi:10.1212/wnl.58.6.881. PMID 11914402. S2CID 19632736.
- Bannon MJ, Pruetz B, Manning-Bog AB, Whitty CJ, Michelhaugh SK, Sacchetti P, Granneman JG, Mash DC, Schmidt CJ (april 2002). "Decreased expression of the transcription factor NURR1 in dopamine neurons of cocaine abusers". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 99 (9): 6382–5. Bibcode:2002PNAS...99.6382B. doi:10.1073/pnas.092654299. PMC 122957. PMID 11959923.
- Le WD, Xu P, Jankovic J, Jiang H, Appel SH, Smith RG, Vassilatis DK (januar 2003). "Mutations in NR4A2 associated with familial Parkinson disease". Nature Genetics. 33 (1): 85–9. doi:10.1038/ng1066. PMID 12496759. S2CID 10699494.
- Satoh J, Kuroda Y (decembar 2002). "The constitutive and inducible expression of Nurr1, a key regulator of dopaminergic neuronal differentiation, in human neural and non-neural cell lines". Neuropathology. 22 (4): 219–32. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1789.2002.00460.x. PMID 12564761. S2CID 30708166.
- Iwayama-Shigeno Y, Yamada K, Toyota T, Shimizu H, Hattori E, Yoshitsugu K, Fujisawa T, Yoshida Y, Kobayashi T, Toru M, Kurumaji A, Detera-Wadleigh S, Yoshikawa T (april 2003). "Distribution of haplotypes derived from three common variants of the NR4A2 gene in Japanese patients with schizophrenia". American Journal of Medical Genetics. Part B, Neuropsychiatric Genetics. 118B (1): 20–4. doi:10.1002/ajmg.b.10053. PMID 12627459. S2CID 35675105.
- Kim KS, Kim CH, Hwang DY, Seo H, Chung S, Hong SJ, Lim JK, Anderson T, Isacson O (maj 2003). "Orphan nuclear receptor Nurr1 directly transactivates the promoter activity of the tyrosine hydroxylase gene in a cell-specific manner". Journal of Neurochemistry. 85 (3): 622–34. doi:10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.01671.x. PMID 12694388. S2CID 6219768.
Vanjski linkovi
uredi- Nurr1 nuclear receptor na US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)