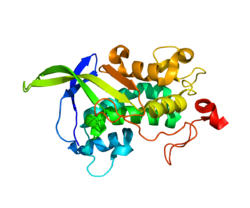
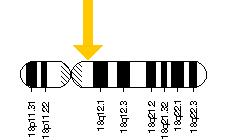
NPC1
Niemann-Pickova bolest tip C1 (NPC1) je bolest membranskog proteina koji kod sisara posreduje u unutarćelijsom prometu holesterola. Kod ljudi protein je kodiran genom NPC1, sa pozicijom 18q11.[5][6]
Dužina polipeptidnog lanca je 1.278 aminokiselina, sa molekulsom težinom od 142.167[7].
Aminokiselinska sekvenca
- Simboli
C: Cistein
D: Asparaginska kiselina
E: Glutaminska kiselina
F: Fenilalanin
G: Glicin
H: Histidin
I: Izoleucin
K: Lizin
L: Leucin
M: Metionin
N: Asparagin
P: Prolin
Q: Glutamin
R: Arginin
S: Serin
T: Treonin
V: Valin
W: Triptofan
Y: Tirozin
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MTARGLALGL | LLLLLCPAQV | FSQSCVWYGE | CGIAYGDKRY | NCEYSGPPKP | ||||
| LPKDGYDLVQ | ELCPGFFFGN | VSLCCDVRQL | QTLKDNLQLP | LQFLSRCPSC | ||||
| FYNLLNLFCE | LTCSPRQSQF | LNVTATEDYV | DPVTNQTKTN | VKELQYYVGQ | ||||
| SFANAMYNAC | RDVEAPSSND | KALGLLCGKD | ADACNATNWI | EYMFNKDNGQ | ||||
| APFTITPVFS | DFPVHGMEPM | NNATKGCDES | VDEVTAPCSC | QDCSIVCGPK | ||||
| PQPPPPPAPW | TILGLDAMYV | IMWITYMAFL | LVFFGAFFAV | WCYRKRYFVS | ||||
| EYTPIDSNIA | FSVNASDKGE | ASCCDPVSAA | FEGCLRRLFT | RWGSFCVRNP | ||||
| GCVIFFSLVF | ITACSSGLVF | VRVTTNPVDL | WSAPSSQARL | EKEYFDQHFG | ||||
| PFFRTEQLII | RAPLTDKHIY | QPYPSGADVP | FGPPLDIQIL | HQVLDLQIAI | ||||
| ENITASYDNE | TVTLQDICLA | PLSPYNTNCT | ILSVLNYFQN | SHSVLDHKKG | ||||
| DDFFVYADYH | THFLYCVRAP | ASLNDTSLLH | DPCLGTFGGP | VFPWLVLGGY | ||||
| DDQNYNNATA | LVITFPVNNY | YNDTEKLQRA | QAWEKEFINF | VKNYKNPNLT | ||||
| ISFTAERSIE | DELNRESDSD | VFTVVISYAI | MFLYISLALG | HMKSCRRLLV | ||||
| DSKVSLGIAG | ILIVLSSVAC | SLGVFSYIGL | PLTLIVIEVI | PFLVLAVGVD | ||||
| NIFILVQAYQ | RDERLQGETL | DQQLGRVLGE | VAPSMFLSSF | SETVAFFLGA | ||||
| LSVMPAVHTF | SLFAGLAVFI | DFLLQITCFV | SLLGLDIKRQ | EKNRLDIFCC | ||||
| VRGAEDGTSV | QASESCLFRF | FKNSYSPLLL | KDWMRPIVIA | IFVGVLSFSI | ||||
| AVLNKVDIGL | DQSLSMPDDS | YMVDYFKSIS | QYLHAGPPVY | FVLEEGHDYT | ||||
| SSKGQNMVCG | GMGCNNDSLV | QQIFNAAQLD | NYTRIGFAPS | SWIDDYFDWV | ||||
| KPQSSCCRVD | NITDQFCNAS | VVDPACVRCR | PLTPEGKQRP | QGGDFMRFLP | ||||
| MFLSDNPNPK | CGKGGHAAYS | SAVNILLGHG | TRVGATYFMT | YHTVLQTSAD | ||||
| FIDALKKARL | IASNVTETMG | INGSAYRVFP | YSVFYVFYEQ | YLTIIDDTIF | ||||
| NLGVSLGAIF | LVTMVLLGCE | LWSAVIMCAT | IAMVLVNMFG | VMWLWGISLN | ||||
| AVSLVNLVMS | CGISVEFCSH | ITRAFTVSMK | GSRVERAEEA | LAHMGSSVFS | ||||
| GITLTKFGGI | VVLAFAKSQI | FQIFYFRMYL | AMVLLGATHG | LIFLPVLLSY | ||||
| IGPSVNKAKS | CATEERYKGT | ERERLLNF |
Funkcija
urediNPC1 je identificiran kao gen čija mutacija izaziva Niemann-Pickovu bolest tip C. Niemann-Pick-ova bolest, tip C, rijedak je neurovisceralni poremećaj skladištenja lipida, koji je posljedica autosomnih recesivno naslijeđenih mutacija gubitka funkcije bilo u NPC1 ili NPC2. To remeti unutarćelijski transport lipida, što dovodi do akumulacije lipidnih produkata u kasnim endosomima i lizosomima. Otkriveno je da približno 95% NPC pacijenata ima mutacije u genu NPC1.
NPC1 kodira pretpostavljeni integralni membranski protein koji sadrži motiv sekvence u skladu s ulogom u unutarćelijskom transportu holesterola do odredišta nakon lizosoma.[5][8]
Klinički značaj
urediGojaznost
urediMutacije u genu NPC1 snažno su povezane sa gojaznosti.[9] Istraživanje povezanosti u genomu identificiralo je mutacije NPC1 kao faktor rizika kod dječje gojaznosti i morbidne gojaznosti odraslih i 1.416 starosne dobi odgovarajuće kontrole normalne težine.[9] Mutacije u NPC1 također su bile u korelaciji sa uobičajenim prirastom težine u populaciji. Prethodne studije na miševima sugerirale su da gen NPC1 ima ulogu u kontroli apetita, budući da miševi s nefunkcionalnim genom NPC1 kasno počinju gubiti težinu i slabo unose hranu. Varijanta gena NPC1 mogla bi predstavljati oko 10 % ukupne dječje pretilosti i oko 14 % odraslih slučajeva morbidne pretilosti.[9]
HIV-AIDS
urediPutevi holesterola imaju važnu ulogu u više faza tokom ciklusa infekcije HIV-1. Fuzija, ulazak, sastavljanje i pupanje HIV-1 dolazi do mikrodomena obogaćenih holesterolom, zvanih lipidni splav. Dokazano je da proteinski pribor za HIV-1, Nef, inducira mnoge gene koji su uključeni u biosintezu i homeostazu holesterola. Unutarćelijski putevi prometa holesterola, posredovani NPC1-om, potrebni su za efikasnu proizvodnju HIV-1.[10][11]
Ebola virus
urediČini se da je ljudski transporter holesterola Niemann-Pickove bolesti C1 (NPC1) ključan za infekciju virusom ebole: niz nezavisnih studija iznijele su dokaze da virus ebole ulazi u ljudske ćelije nakon vezanja za NPC1.[12][13] Kada su ćelije pacijenata kojima ovaj transporter u laboratoriji nije bio izloženi virusu ebole, one su preživjele i izgledale nepropusno za virus, što dalje ukazuje da se ebola, za ulaz u ćelije, oslanja na NPC1.[13] Iste studije su opisale slične rezultate sa Marburg virusom, drugim filovirusom, pokazujući da i njemu treba NPC1 za ulazak u ćelije.[13] U jednoj od studija pokazalo se da je NPC1 presudan za ulazak u filovirusa, jer posreduje infekciju, vežući se direktno za glikoproteinsku virusnu ovojnicu.[13] A kasnija studija potvrdila je nalaze da je NPC1 kritični filovirusni receptor koji posreduje infekciju, vežući se direktno za virusnu ovojnicu i da u ovom vezanju posreduje drugi lizosomski domen NPC1.[14]
U jednoj od originalnih studija pokazano je da mala molekula inhibira infekciju virusom ebole, sprečavajući da se virusni glikoprotein veže za NPC1.[13][15] U drugoj studiji pokazalo se da su heterozigotni miševi za NPC1 zaštićeni od smrtonosnog izazivanja za miševe prilagođenim virusom ebole.[12] Zajedno, ove studije sugeriraju da NPC1 može biti potencijalni terapijski cilj za antivirusni lijek protiv ebole.
Mehanizmi u patologiji
urediU modelu miša koji nosi osnovnu mutaciju za Niemann–Pickovu bolest tip C1 u NPC1 proteinu, pokazalo se da je ekspresija regulatornog faktora mijelinskog gena (MRF) značajno smanjena.[16] Regulatorni faktor gena za mijelin (MRF) je faktor transkripcije od presudne važnosti u razvoju i održavanju mijelinskih ovojnica.[17] Perturbacija sazrijevanja oligodendrocita i proces mijelinizacije mogu stoga biti osnovni mehanizam neuroloških deficita.[16]
Reference
uredi- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000141458 - Ensembl, maj 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000024413 - Ensembl, maj 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ a b "Entrez Gene: NPC1 Niemann-Pick disease, type C1".
- ^ Carstea ED, Polymeropoulos MH, Parker CC, Detera-Wadleigh SD, O'Neill RR, Patterson MC, et al. (mart 1993). "Linkage of Niemann-Pick disease type C to human chromosome 18". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 90 (5): 2002–4. Bibcode:1993PNAS...90.2002C. doi:10.1073/pnas.90.5.2002. PMC 46008. PMID 8446622.
- ^ "UniProt, O15118". Pristupljeno 12. 9. 2017.
- ^ Carstea ED, Morris JA, Coleman KG, Loftus SK, Zhang D, Cummings C, et al. (juli 1997). "Niemann-Pick C1 disease gene: homology to mediators of cholesterol homeostasis". Science. 277 (5323): 228–31. doi:10.1126/science.277.5323.228. PMID 9211849.
- ^ a b c Meyre D, Delplanque J, Chèvre JC, Lecoeur C, Lobbens S, Gallina S, et al. (februar 2009). "Genome-wide association study for early-onset and morbid adult obesity identifies three new risk loci in European populations". Nature Genetics. 41 (2): 157–9. doi:10.1038/ng.301. PMID 19151714. S2CID 11218794.
- ^ Tang Y, Leao IC, Coleman EM, Broughton RS, Hildreth JE (august 2009). "Deficiency of niemann-pick type C-1 protein impairs release of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 and results in Gag accumulation in late endosomal/lysosomal compartments". Journal of Virology. 83 (16): 7982–95. doi:10.1128/JVI.00259-09. PMC 2715784. PMID 19474101.
- ^ Coleman EM, Walker TN, Hildreth JE (januar 2012). "Loss of Niemann Pick type C proteins 1 and 2 greatly enhances HIV infectivity and is associated with accumulation of HIV Gag and cholesterol in late endosomes/lysosomes". Virology Journal. 9 (1): 31. doi:10.1186/1743-422X-9-31. PMC 3299633. PMID 22273177.
- ^ a b Carette JE, Raaben M, Wong AC, Herbert AS, Obernosterer G, Mulherkar N, et al. (august 2011). "Ebola virus entry requires the cholesterol transporter Niemann-Pick C1". Nature. 477 (7364): 340–3. Bibcode:2011Natur.477..340C. doi:10.1038/nature10348. PMC 3175325. PMID 21866103. Sažetak – New York Times.
- ^ a b c d e Côté M, Misasi J, Ren T, Bruchez A, Lee K, Filone CM, et al. (august 2011). "Small molecule inhibitors reveal Niemann-Pick C1 is essential for Ebola virus infection". Nature. 477 (7364): 344–8. Bibcode:2011Natur.477..344C. doi:10.1038/nature10380. PMC 3230319. PMID 21866101. Sažetak – New York Times.
- ^ Miller EH, Obernosterer G, Raaben M, Herbert AS, Deffieu MS, Krishnan A, et al. (april 2012). "Ebola virus entry requires the host-programmed recognition of an intracellular receptor". The EMBO Journal. 31 (8): 1947–60. doi:10.1038/emboj.2012.53. PMC 3343336. PMID 22395071.
- ^ Flemming A (septembar 2011). "Achilles heel of Ebola viral entry". Nature Reviews. Drug Discovery. 10 (10): 731. doi:10.1038/nrd3568. PMID 21959282. S2CID 26888076.
- ^ a b Yan X, Lukas J, Witt M, Wree A, Hübner R, Frech M, et al. (decembar 2011). "Decreased expression of myelin gene regulatory factor in Niemann-Pick type C 1 mouse". Metabolic Brain Disease. 26 (4): 299–306. doi:10.1007/s11011-011-9263-9. PMID 21938520. S2CID 26878522.
- ^ Koenning M, Jackson S, Hay CM, Faux C, Kilpatrick TJ, Willingham M, Emery B (septembar 2012). "Myelin gene regulatory factor is required for maintenance of myelin and mature oligodendrocyte identity in the adult CNS". The Journal of Neuroscience. 32 (36): 12528–42. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1069-12.2012. PMC 3752083. PMID 22956843.
Dopunska literatura
uredi- Vanier MT, Suzuki K (januar 1998). "Recent advances in elucidating Niemann-Pick C disease". Brain Pathology. 8 (1): 163–74. doi:10.1111/j.1750-3639.1998.tb00143.x. PMID 9458174. S2CID 10300500.
- Liscum L, Klansek JJ (april 1998). "Niemann-Pick disease type C". Current Opinion in Lipidology. 9 (2): 131–5. doi:10.1097/00041433-199804000-00009. PMID 9559270.
- Morris JA, Carstea ED (decembar 1998). "Niemann-Pick C disease: cholesterol handling gone awry". Molecular Medicine Today. 4 (12): 525–31. doi:10.1016/S1357-4310(98)01374-4. PMID 9866822.
- Garver WS, Heidenreich RA (august 2002). "The Niemann-Pick C proteins and trafficking of cholesterol through the late endosomal/lysosomal system". Current Molecular Medicine. 2 (5): 485–505. doi:10.2174/1566524023362375. PMID 12125814.
- Greer WL, Riddell DC, Byers DM, Welch JP, Girouard GS, Sparrow SM, et al. (juli 1997). "Linkage of Niemann-Pick disease type D to the same region of human chromosome 18 as Niemann-Pick disease type C". American Journal of Human Genetics. 61 (1): 139–42. doi:10.1086/513899. PMC 1715879. PMID 9245994.
- Greer WL, Riddell DC, Gillan TL, Girouard GS, Sparrow SM, Byers DM, et al. (juli 1998). "The Nova Scotia (type D) form of Niemann-Pick disease is caused by a G3097-->T transversion in NPC1". American Journal of Human Genetics. 63 (1): 52–4. doi:10.1086/301931. PMC 1377252. PMID 9634529.
- Watari H, Blanchette-Mackie EJ, Dwyer NK, Glick JM, Patel S, Neufeld EB, et al. (februar 1999). "Niemann-Pick C1 protein: obligatory roles for N-terminal domains and lysosomal targeting in cholesterol mobilization". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 96 (3): 805–10. Bibcode:1999PNAS...96..805W. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.3.805. PMC 15306. PMID 9927649.
- Patel SC, Suresh S, Kumar U, Hu CY, Cooney A, Blanchette-Mackie EJ, et al. (februar 1999). "Localization of Niemann-Pick C1 protein in astrocytes: implications for neuronal degeneration in Niemann- Pick type C disease". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 96 (4): 1657–62. Bibcode:1999PNAS...96.1657P. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.4.1657. PMC 15549. PMID 9990080.
- Morris JA, Zhang D, Coleman KG, Nagle J, Pentchev PG, Carstea ED (august 1999). "The genomic organization and polymorphism analysis of the human Niemann-Pick C1 gene". Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 261 (2): 493–8. doi:10.1006/bbrc.1999.1070. PMID 10425213.
- Yamamoto T, Nanba E, Ninomiya H, Higaki K, Taniguchi M, Zhang H, et al. (1999). "NPC1 gene mutations in Japanese patients with Niemann-Pick disease type C". Human Genetics. 105 (1–2): 10–6. doi:10.1007/s004390051057. PMID 10480349.
- Greer WL, Dobson MJ, Girouard GS, Byers DM, Riddell DC, Neumann PE (novembar 1999). "Mutations in NPC1 highlight a conserved NPC1-specific cysteine-rich domain". American Journal of Human Genetics. 65 (5): 1252–60. doi:10.1086/302620. PMC 1288277. PMID 10521290.
- Millat G, Marçais C, Rafi MA, Yamamoto T, Morris JA, Pentchev PG, et al. (novembar 1999). "Niemann-Pick C1 disease: the I1061T substitution is a frequent mutant allele in patients of Western European descent and correlates with a classic juvenile phenotype". American Journal of Human Genetics. 65 (5): 1321–9. doi:10.1086/302626. PMC 1288284. PMID 10521297.
- Davies JP, Ioannou YA (august 2000). "Topological analysis of Niemann-Pick C1 protein reveals that the membrane orientation of the putative sterol-sensing domain is identical to those of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase and sterol regulatory element binding protein cleavage-activating protein". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 275 (32): 24367–74. doi:10.1074/jbc.M002184200. PMID 10821832.
- Millat G, Marçais C, Tomasetto C, Chikh K, Fensom AH, Harzer K, et al. (juni 2001). "Niemann-Pick C1 disease: correlations between NPC1 mutations, levels of NPC1 protein, and phenotypes emphasize the functional significance of the putative sterol-sensing domain and of the cysteine-rich luminal loop". American Journal of Human Genetics. 68 (6): 1373–85. doi:10.1086/320606. PMC 1226124. PMID 11333381.
- Sun X, Marks DL, Park WD, Wheatley CL, Puri V, O'Brien JF, et al. (juni 2001). "Niemann-Pick C variant detection by altered sphingolipid trafficking and correlation with mutations within a specific domain of NPC1". American Journal of Human Genetics. 68 (6): 1361–72. doi:10.1086/320599. PMC 1226123. PMID 11349231.
Vanjski linkovi
uredi- NPC1 protein, human na US National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- Fight NPC, a website dedicated to providing information and resources on treating Niemann–Pick type C disease Arhivirano 5. 6. 2021. na Wayback Machine
- Hide & Seek Foundation for Lysosomal Disease Research