Korisnik:Palapa/ARPANET
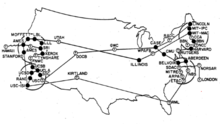
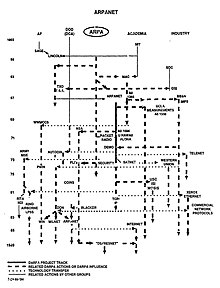
Advanced Research Projects Agency Network, u prijevodu Mreža agencija za napredne istraživačke projekte (ARPANET) bila je prva mreža sa komutacijom paketa širokog područja sa distribuiranom kontrolom i jedna od prvih mreža koja je implementirala paket TCP/IP protokola. Obje tehnologije postale su tehnički temelj Interneta. ARPANET je osnovala Agencija za napredne istraživačke projekte (ARPA) Ministarstva odbrane Sjedinjenih Država.[1]
Nadovezujući se na ideje J. C. R. Licklidera, Bob Taylor je 1966. godine pokrenuo projekat ARPANET kako bi omogućio dijeljenje resursa između udaljenih računara.[2] Taylor je imenovao Larryja Robertsa za menadžera programa. Roberts je donio ključne odluke o dizajnu mreže.[3] Ugradio je koncepte i dizajne Donalda Daviesa za komutaciju paketa,[4] [5] i zatražio pomoć od Paula Barana.[6] ARPA je dodijelila ugovor za izgradnju mreže Boltu Beranek & Newmanu koji su razvili prvi protokol za mrežu. [7] Roberts je angažovao Leonarda Kleinrocka na UCLA da razvije matematičke metode za analizu tehnologije paketne mreže.[6]
Prvi računari su povezani 1969. godine, a protokol mrežne kontrole implementiran je 1970.[8] [9] Mreža je proglašena operativnom 1971. godine. Dalji razvoj softvera omogućio je udaljenu prijavu, prijenos datoteka i e-mail.[10] Mreža se brzo širila i operativna kontrola je 1975. prešla na Agenciju za obrambene komunikacije.

Reference
uredi- ^ "ARPANET – The First Internet". Living Internet. Pristupljeno 2021-03-19.
- ^ "An Internet Pioneer Ponders the Next Revolution". The New York Times. December 20, 1999. Pristupljeno 2020-02-20.
Mr. Taylor wrote a white paper in 1968, a year before the network was created, with another ARPA research director, J. C. R. Licklider. The paper, "The Computer as a Communications Device," was one of the first clear statements about the potential of a computer network.
- ^ Hafner, Katie (2018-12-30). "Lawrence Roberts, Who Helped Design Internet's Precursor, Dies at 81". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Pristupljeno 2020-02-20.
He decided to use packet switching as the underlying technology of the Arpanet; it remains central to the function of the internet. And it was Dr. Roberts's decision to build a network that distributed control of the network across multiple computers. Distributed networking remains another foundation of today's internet.
- ^ "Computer Pioneers - Donald W. Davies". IEEE Computer Society. Pristupljeno 2020-02-20.
In 1965, Davies pioneered new concepts for computer communications in a form to which he gave the name "packet switching." ... The design of the ARPA network (ArpaNet) was entirely changed to adopt this technique.
- ^ "A Flaw In The Design". The Washington Post. May 30, 2015.
The Internet was born of a big idea: Messages could be chopped into chunks, sent through a network in a series of transmissions, then reassembled by destination computers quickly and efficiently. Historians credit seminal insights to Welsh scientist Donald W. Davies and American engineer Paul Baran. ... The most important institutional force ... was the Pentagon's Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA) ... as ARPA began work on a groundbreaking computer network, the agency recruited scientists affiliated with the nation's top universities.
- ^ a b Abbate, Janet (2000). Inventing the Internet. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press. str. 39, 57–58. ISBN 978-0-2625-1115-5.
Baran proposed a "distributed adaptive message-block network" [in the early 1960s] ... Roberts recruited Baran to advise the ARPANET planning group on distributed communications and packet switching. ... Roberts awarded a contract to Leonard Kleinrock of UCLA to create theoretical models of the network and to analyze its actual performance.
- ^ Roberts, Lawrence G. (November 1978). "The Evolution of Packet Switching" (PDF). IEEE Invited Paper. Arhivirano s originala (PDF), 31 December 2018. Pristupljeno September 10, 2017.
Significant aspects of the network's internal operation, such as routing, flow control, software design, and network control were developed by a BBN team consisting of Frank Heart, Robert Kahn, Severo Omstein, William Crowther, and David Walden
- ^ Bidgoli, Hossein (2004-05-11). The Internet Encyclopedia, Volume 2 (G - O) (jezik: engleski). John Wiley & Sons. str. 39. ISBN 978-0-471-68996-6.
- ^ Coffman, K. G.; Odlyzco, A. M. (2002). "Growth of the Internet". u Kaminow, I.; Li, T. (ured.). Optical Fiber Telecommunications IV-B: Systems and Impairments. Academic Press. ISBN 978-0123951731. Pristupljeno 15 August 2015.
- ^ Lievrouw, L. A. (2006). Lievrouw, L. A.; Livingstone, S. M. (ured.). Handbook of New Media: Student Edition. SAGE. str. 253. ISBN 1412918731. Pristupljeno 15 August 2015.